fjt_072844 - CORPORATIONS Jeton Ar 30, marchands-passementiers n.d.
Not available.
Item sold on our e-shop
Price : 28.00 €
Item sold on our e-shop
Price : 28.00 €
Type : Jeton Ar 30, marchands-passementiers
Date: n.d.
Metal : silver
Diameter : 30,5 mm
Orientation dies : 6 h.
Weight : 8,63 g.
Edge : cannelée
Rarity : R1
Coments on the condition:
Forte usure de circulation au droit et au revers. Patine noire
Catalogue references :
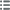
Obverse
Obverse legend : LUD. XV. REX - CHRISTIANISS..
Obverse description : Tête ceinte d’un bandeau à droite de Louis XV [n° 322] ; au-dessous signature cursive fm.
Obverse translation : (Louis XV roi très chrétien).
Reverse
Reverse description : La Sainte Vierge baignant l'enfant Jésus ; devant elle, sa mère couchée sur un lit et derrière une figure préparant une couverture ; à l'exergue en quatre lignes : ETABLISSEMENT ROYAL DES/ MARCH. PASSEMENTIERS/ DE ROUEN EN/ 1531.
Commentary
Les marchands passementiers fabriquent et vendent des articles tissés ou tressés (passements, franges, galons, etc.) utilisés comme garniture dans l'ameublement ou, plus rarement, dans l'habillement.








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data















