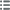
Obverse
Obverse legend : RÉPUBLIQUE - * FRANÇAISE.
Obverse description : Tête de la République à gauche en Cérès, déesse des moissons, portant un collier de perles, un double chignon et une couronne composite de blé, fleurs, olivier et olives, chêne et glands, nouée par un ruban descendant sur le cou et passant sur le front où est inscrit le mot CONCORDE ; sous la tranche du cou le long du listel : E. A. OUDINÉ. F..
Reverse
Reverse legend : L’AN MDCCCLXXXV / LE III AOÛT / M.R JULES GRÉVY / ÉTANT PRÉSIDENT / DE LA RÉPUBLIQUE FRANÇAISE / M.R RENE GOBLET / MINISTRE DE L’INSTRUCTION PUBLIQUE / DES BEAUX-ARTS ET DES CULTES / ASSISTE DE M.R GRÉARD VICE-RECTEUR / DE L’ACADÉMIE DE PARIS MEMBRE DE L’INSTITUT / EN PRÉSENCE DE MM.RS / POUBELLE / PRÉFET DE LA SEINE // MICHELIN / P.T DU CONSEIL MUNICIP.L / A POSE LA PREMIÈRE PIERRE DE / LA SORBONNE / RECONSTRUITE ET AGRANDIE / A FRAIS COMMUNS / PAR L’ÉTAT ET LA VILLE DE PARIS / - / H. PAUL NENOT ARCH.TE.
Reverse description : Légende en 19 lignes horizontales.
Historical background
III REPUBLIC
(4/09/1870-10/07/1940)
The news of the capitulation of Sedan provokes the revolution of September 4, 1870 in Paris. Proclaimed at the Hôtel de Ville, the Republic is endowed with a provisional government called the Government of National Defense. Threatened on the left by the insurrection of the Commune and on the right by the monarchists, the new regime had a difficult start.. Initially head of the executive power (February 1871), Thiers was responsible for reorganizing the country before choosing its form of government.. He became President of the Republic in August 1871 and, despite his action to liberate the territory, had to leave his post in March 1873 in the face of royalist opposition.. He is then replaced by Mac-Mahon favorable to the restoration of the monarchy but this one is not restored following the question of the flag. The law of the septennat was then put in place in November 1873 and then, in 1875, the fundamental laws were passed which served as the Constitution of the Third Republic.. Parliamentary system, it is characterized in particular by the clear preponderance of the legislative power on the executive power. Anticlerical, the Third Republic makes school free, secular and compulsory but continues the colonial policy for its economic, strategic and moral ambitions. Separation of Church and State was passed in 1905.. The idea of revenge on Germany and significant nationalism are at the heart of the Boulangist crisis, the Panama scandal or the Dreyfus affair of the years 1886-1899, while foreign policy is very active, particularly in Morocco and that the arms race develops. The First World War was expensive for France, which only recovered from 1920 or even 1928 for the coin with the "Poincaré" franc.. The crisis of 1929 is felt only from 1932 but lasts until 1939, a period during which ministerial instability is very important. Wavering in 1934, the Third Republic found a new unitary cement with anti-fascism which enabled the Popular Front to come to power in 1936.. But, paralyzed against Germany, France was then bogged down in a "phony war" and then suffered one of the greatest defeats in its history in June 1940.. Gathered in the National Assembly in Vichy on July 10, 1940, the Chambers, although elected in 1936, voted full powers to Pétain in a sort of collective suicide by 569 votes for, 80 votes against and 18 abstentions..










 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data



