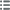
Obverse
Obverse legend : M.
Obverse description : Tête laurée d’Apollon à gauche, les cheveux longs.
Reverse
Reverse description : Dauphin à gauche.
Commentary
Historical background
MASSALIA - MARSEILLE
(5th - 1st century BC)
Marseille, the "Massalia" of the Greeks, founded by the Phocaeans in 600 BC. -VS. , was born from the desire of the Greeks to promote trading posts in order to compete with the Carthaginians and the Etruscans for the domination of the western Mediterranean. Marseille is absolutely not a Celtic or Gallic creation and belongs to the Greek world. Between the 5th and 1st centuries BC, Marseille and its hinterland experienced unprecedented development. The rise of Rome from the First Punic War (268-241 BC). -VS. ), and the strategic choice of Marseilles, which plays Rome against Carthage, will restore, in the second half of the third century BC, a preponderant role to Massalia in the international trade of the western Mediterranean.. The second century BC marks the decline of the Phocaean city. Privileged ally of the Romans, Marseille has, thanks to them, succeeded in imposing its power in the Marseille hinterland. The Romans, by stopping the Cimbri and the Teutons, saved southern Gaul from invasions. From 118 BC. -VS. , the situation changes and the Provincia becomes a Roman province. Marseille merchants compete with Roman traders in Spain, Corsica, Sardinia and Sicily. Nevertheless, they remain the allies of the Romans until the 1st century BC.. This is the beginning of the civil war between Caesar and Pompey in 49 BC.. -VS. which will be fatal to the city. Marseille did not know how to choose between the two protagonists. Caesar besieged and took the city, not being able to allow his lines of communication between Gaul and Italy to be cut off.. Marseille's fleet was still too large to fall into the hands of his mortal enemy, Pompey. Conquered, the city was nevertheless not plundered and remained an important port at the beginning of the Roman domination. Remaining Hellenic, it was never really assimilated to Roman Gaul and kept a sort of independent status, mixed with cosmopolitanism where all religions crossed paths with all peoples for the greater benefit of Marseille trade..








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data



