bga_239112 - MASSALIA - MARSEILLE Diobole à l’aigle, B
Not available.
Item sold on our e-shop (2011)
Price : 500.00 €
Item sold on our e-shop (2011)
Price : 500.00 €
Type : Diobole à l’aigle, B
Date: c. 220-90 AC.
Mint name / Town : Marseille (13)
Metal : silver
Diameter : 12 mm
Orientation dies : 4 h.
Weight : 0,86 g.
Rarity : R3
Coments on the condition:
Monnaie bien frappée sur un flan large, avec un droit et un revers un peu décalés mais presque complets. Patine grise sur un bon métal
Catalogue references :
Predigree :
Cet exemplaire provient de la collection M. G
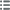
Obverse
Obverse legend : DERRIÈRE LE CIMIER.
Obverse description : Tête d’Athéna casquée à droite ; grènetis.
Obverse legend : B.
Reverse
Reverse description : devant un aigle posé à droite, l’aile ouverte.
Reverse legend : MASSA.
Commentary
Toutes variétés confondues, cet exemplaire n’est que le quatrième diobole que nous proposions à la vente, après celui de MONNAIES II (A), celui de MONNAIES 29 (B) et de MONNAIES 45 (B).
G. Depeyrot a répertorié 20 exemplaires pour la variété avec le A et autant pour la variété avec le B. Les poids sont répartis entre 0,73 et 0,96 pour un poids moyen de 0,84 gramme. L'alliage des dioboles n'a que très peu de cuivre par rapport à celui des oboles ; les dioboles ont soit une forte proportion de fer, soit pas de fer.
Cet exemplaire de la variété B est dans un très bel état, tant de frappe que de conservation, pour ce très rare monnayage !.
G. Depeyrot a répertorié 20 exemplaires pour la variété avec le A et autant pour la variété avec le B. Les poids sont répartis entre 0,73 et 0,96 pour un poids moyen de 0,84 gramme. L'alliage des dioboles n'a que très peu de cuivre par rapport à celui des oboles ; les dioboles ont soit une forte proportion de fer, soit pas de fer.
Cet exemplaire de la variété B est dans un très bel état, tant de frappe que de conservation, pour ce très rare monnayage !.








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data



