fjt_791699 - DIJON (MAYORS OF ... and miscellaneous) Jean Tisserand 1624
30.00 €(Approx. 35.40$ | 26.10£)
Quantity
Add to your cart

Type : Jean Tisserand
Date: 1624
Metal : brass
Diameter : 27 mm
Orientation dies : 6 h.
Weight : 6,10 g.
Edge : lisse
Rarity : R1
Catalogue references :
Predigree :
Exemplaire provenant de la Collection MARINECHE
Obverse
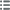
Obverse legend : * I. TISSERAND. C. D. R. LIEVT. EN. LA. CHANC. VIC. M. DE. DIION.
Obverse description : Armes de Dijon dans une couronne de laurier.
Reverse
Reverse legend : QVI. SVA. METITVR. PONDERA. FERRE. POTEST. 1624..
Reverse description : Armes lambrequinées.
Commentary
Jean Tisserand fut continué maire en 1624. Sous son mandat, il présida la réunion des échevins du 13 mai 1625 qui délibéra sur la sédition de la veille, lors de l’exécution d’Hélène Gillet, à la suite de laquelle le bourreau et sa femme furent tués par le peuple à coups de pierres, de marteaux et de poignards
Les maires de Dijon
Dès l’époque de la naissance de la féodalité, la ville de Dijon possédait un maire et en général vingt magistrats municipaux, ou échevins. Ces magistrats sont confirmés en 1187, lorsqu’une charte de commune est accordée par le duc Hugues III. En 1192, pour la première fois, le maire dijonnais est élu.
A la fin du XIIIe siècle, ce maire prend le titre de vicomte maïeur, confirmé en 1477-1479 par Louis XI, qu’il gardera jusqu’en 1789. Depuis la fin du XVe siècle (1491), la charge de vicomte maïeur est anoblissante ainsi que celle d’échevin à compter du XVIe siècle. Le vicomte maïeur avait le droit de haute, moyenne et basse justice, le droit de scel et de visite. Les clefs de la ville lui sont confiées et il dirige les archers ainsi que les compagnies des sept quartiers, cette fonction militaire étant importante jusqu’au XVIIe siècle.
Fonction élective, le vicomte maïeur est élu par les habitants, ni mendiants, ni étrangers, qui payent la taille, en général la veille de la Saint-Jean. Cette élection a lieu sur le parvis de l'église saint Philibert. A partir de 1669, il est permis au maire de porter "une robe longue de satin plein, de couleur violet, doublée de satin rouge cramoisi, comme le prévôt des marchands de Lyon, avec chaperon de même étoffe et couleur bordée d’hermine" afin de se distinguer des habitants.
En 1692, la fonction de vicomte maïeur est transformée en office héréditaire tandis que l’élection n’est plus alors qu’une confirmation du choix royal fait par le gouverneur au nom du roi.
Voir leur liste complète à http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liste_des_maires_de_Dijon.
Jean Tisserand was continued as mayor in 1624. During his term of office, he chaired the meeting of aldermen on 13 May 1625 which deliberated on the sedition of the previous day, during the execution of Hélène Gillet, following which the executioner and his wife were killed by the people with stones, hammers and daggers. The mayors of Dijon From the time of the birth of feudalism, the city of Dijon had a mayor and generally twenty municipal magistrates, or aldermen.. These magistrates were confirmed in 1187, when a municipal charter was granted by Duke Hugh III.. In 1192, for the first time, the mayor of Dijon was elected.
At the end of the 13th century, this mayor took the title of viscount mayor, confirmed in 1477-1479 by Louis XI, which he kept until 1789.. Since the end of the 15th century (1491), the position of viscount mayor has been ennobling, as has that of alderman since the 16th century.. The Viscount Mayor had the right of high, middle and low justice, the right of seal and visitation. The keys to the city were entrusted to him and he commanded the archers as well as the companies of the seven districts, this military function being important until the 17th century..
An elective function, the Viscount Mayor is elected by the inhabitants, neither beggars nor foreigners, who pay the tax, generally on the eve of Saint John.. This election takes place on the forecourt of the Saint Philibert church. From 1669, the mayor was allowed to wear \\\"a long robe of full satin, purple in color, lined with crimson red satin, like the provost of the merchants of Lyon, with a chaperon of the same fabric and color edged with ermine\\\" in order to distinguish himself from the inhabitants..
In 1692, the function of Viscount Mayor was transformed into a hereditary office while the election was then only a confirmation of the royal choice made by the governor in the name of the king..
See their full list at http://fr. Wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_mayors_of_Dijon
Les maires de Dijon
Dès l’époque de la naissance de la féodalité, la ville de Dijon possédait un maire et en général vingt magistrats municipaux, ou échevins. Ces magistrats sont confirmés en 1187, lorsqu’une charte de commune est accordée par le duc Hugues III. En 1192, pour la première fois, le maire dijonnais est élu.
A la fin du XIIIe siècle, ce maire prend le titre de vicomte maïeur, confirmé en 1477-1479 par Louis XI, qu’il gardera jusqu’en 1789. Depuis la fin du XVe siècle (1491), la charge de vicomte maïeur est anoblissante ainsi que celle d’échevin à compter du XVIe siècle. Le vicomte maïeur avait le droit de haute, moyenne et basse justice, le droit de scel et de visite. Les clefs de la ville lui sont confiées et il dirige les archers ainsi que les compagnies des sept quartiers, cette fonction militaire étant importante jusqu’au XVIIe siècle.
Fonction élective, le vicomte maïeur est élu par les habitants, ni mendiants, ni étrangers, qui payent la taille, en général la veille de la Saint-Jean. Cette élection a lieu sur le parvis de l'église saint Philibert. A partir de 1669, il est permis au maire de porter "une robe longue de satin plein, de couleur violet, doublée de satin rouge cramoisi, comme le prévôt des marchands de Lyon, avec chaperon de même étoffe et couleur bordée d’hermine" afin de se distinguer des habitants.
En 1692, la fonction de vicomte maïeur est transformée en office héréditaire tandis que l’élection n’est plus alors qu’une confirmation du choix royal fait par le gouverneur au nom du roi.
Voir leur liste complète à http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liste_des_maires_de_Dijon.
Jean Tisserand was continued as mayor in 1624. During his term of office, he chaired the meeting of aldermen on 13 May 1625 which deliberated on the sedition of the previous day, during the execution of Hélène Gillet, following which the executioner and his wife were killed by the people with stones, hammers and daggers. The mayors of Dijon From the time of the birth of feudalism, the city of Dijon had a mayor and generally twenty municipal magistrates, or aldermen.. These magistrates were confirmed in 1187, when a municipal charter was granted by Duke Hugh III.. In 1192, for the first time, the mayor of Dijon was elected.
At the end of the 13th century, this mayor took the title of viscount mayor, confirmed in 1477-1479 by Louis XI, which he kept until 1789.. Since the end of the 15th century (1491), the position of viscount mayor has been ennobling, as has that of alderman since the 16th century.. The Viscount Mayor had the right of high, middle and low justice, the right of seal and visitation. The keys to the city were entrusted to him and he commanded the archers as well as the companies of the seven districts, this military function being important until the 17th century..
An elective function, the Viscount Mayor is elected by the inhabitants, neither beggars nor foreigners, who pay the tax, generally on the eve of Saint John.. This election takes place on the forecourt of the Saint Philibert church. From 1669, the mayor was allowed to wear \\\"a long robe of full satin, purple in color, lined with crimson red satin, like the provost of the merchants of Lyon, with a chaperon of the same fabric and color edged with ermine\\\" in order to distinguish himself from the inhabitants..
In 1692, the function of Viscount Mayor was transformed into a hereditary office while the election was then only a confirmation of the royal choice made by the governor in the name of the king..
See their full list at http://fr. Wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_mayors_of_Dijon








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data















