E-auction 228-152937 - fjt_02780 - CONSEIL DU ROI / KING'S COUNCIL Louis XIV 1661
You must signin and be an approved bidder to bid, LOGIN TO BID. Accounts are subject to approval and the approval process takes place within 48 hours. Do not wait until the day a sale closes to register. Clicking on « bid » constitutes acceptance of the terms of use of cgb.fr private e-auctions.
Bids must be placed in whole Euro amounts only. The sale will start closing at the time stated on the item description; any bids received at the site after the closing time will not be executed. Transmission times may vary and bids could be rejected if you wait until the last second. For further information ckeck the E-auctions F.A.Q.
NO BUYER'S FEE.
NO BUYER'S FEE.
| Estimate : | 18 € |
| Price : | 8 € |
| Maximum bid : | 11 € |
| End of the sale : | 28 August 2017 18:10:00 |
| bidders : | 3 bidders |
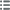
Type : Louis XIV
Date: 1661
Metal : copper
Catalogue references :
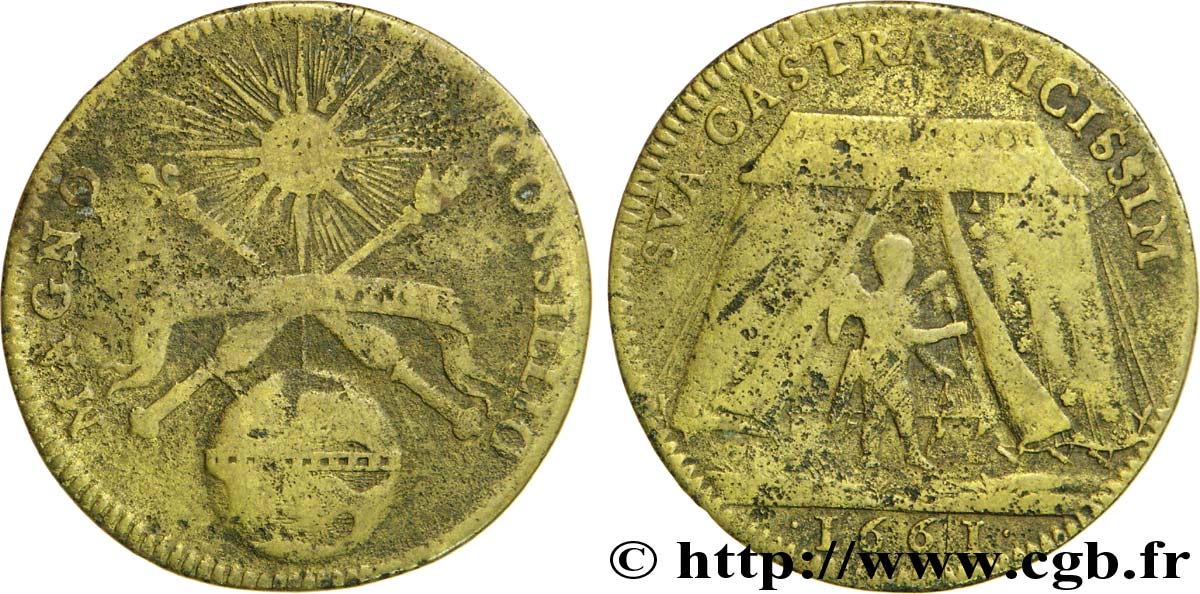
Obverse
Obverse legend : MAGNO CONSILIO.
Obverse description : Sceptre et main de justice en sautoir; dessous, un globe; dessus, le Soleil rayonnant. Une banderole lie le sceptre et la main de justice; sous cette banderole : UNICO. UNIVERSUS (Tout le royaume sous une seule Loi).
Obverse translation : Pour le Grand Conseil.
Reverse
Reverse legend : SUA CASTRA VICISSIM ; À L'EXERGUE : 1661.
Reverse description : L'Amour sous une tente, tenant un arc et une flèche allant à droite.
Reverse translation : Son camp en retour.
Commentary
1661 : réforme du conseil. Le sceptre et la main de Justice évoquent l'aspect judiciaire de cette institution. Les affaires multiples dont avait à s'occuper le Conseil du Roi (appelé d'abord Grand Conseil) amena en effet la création par Charles VII en 1497 d'un tribunal permanent qui prit le titre exclusif de Grand Conseil et auquel furent dévolues les attributions judiciaires que l'on enleva au Conseil du Roi. Il était composé du Chancelier de France, des maîtres des requêtes ordinaires de l'Hôtel du Roi et de 17 conseillers ordinaires .








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data















