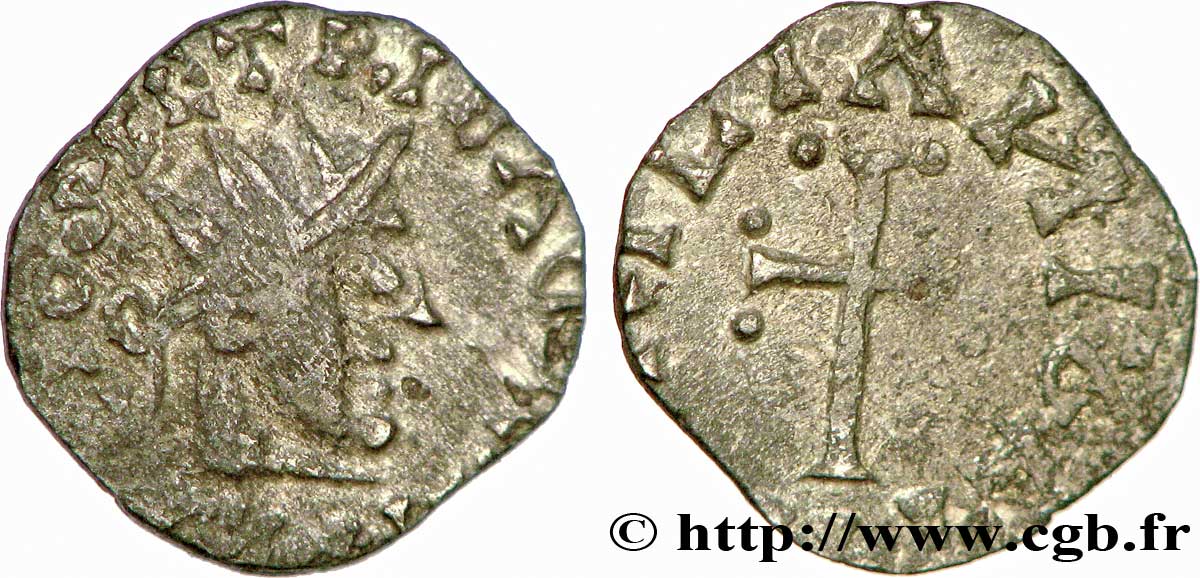
v55_0608 - AURELIANORUM CIVITAS - ORLÉANS (Loiret) Denier, RACIO SCI PETRI
MONNAIES 55 (2012)
Starting price : 650.00 €
Estimate : 1 000.00 €
Realised price : 650.00 €
Starting price : 650.00 €
Estimate : 1 000.00 €
Realised price : 650.00 €
Type : Denier, RACIO SCI PETRI
Date: c. 700-725
Mint name / Town : Orléans (45)
Metal : silver
Diameter : 12 mm
Orientation dies : 12 h.
Weight : 1,03 g.
Rarity : R3
Coments on the condition:
Denier de frappe vigoureuse, sur un flan un peu court mais avec des types centrés. Les légendes sont partiellement hors flan et en bord de flan. Agréable patine grise avec des restes du brillant de frappe
Catalogue references :
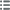
Obverse
Obverse legend : + RACIO SIETRI EAC....
Obverse description : Tête radiée à droite ; légende autour.
Reverse
Reverse legend : + [AV]RILIANIS CIV.
Reverse description : Croix latine dont les bras sont accostés de petites perles ; une croisette initiale à la base de la croix ; grènetis.
Commentary
D’un type de revers habituel, cet exemplaire semble devoir être rapproché du n° 543 du Belfort, pour RACIO SCI PETRI, bien que la légende soit incomplète et incertaine par endroits. Le denier B. 543 a une tête à droite et provient de l’un des premiers livres de numismatique illustrés ; le Bouteroue. Si l’orientation est incertaine, la nature de la légende avec (...) IO SCI PETA (...) confirme que nous sommes en présence d’un rare denier de l’atelier d’Orléans, comme indiqué au revers. Le Moneta semble reprendre le denier B. 541 pour RACIO MONASTERI et propose Saint-Pierre pour le denier B. 543 dont le seul exemplaire serait celui du Bouteroue. Notre denier vient confirmer l’existence de ce type et s’intègre entre ces deux deniers, l’un pour Saint-Pierre, l’autre pour le monastère de Saint-Mesmin.








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data