fme_445995 - LOUIS XVI Médaille des raffineries sucrières de Bordeaux
Not available.
Item sold on our e-shop (2019)
Price : 250.00 €
Item sold on our e-shop (2019)
Price : 250.00 €
Type : Médaille des raffineries sucrières de Bordeaux
Date: 1786
Mint name / Town : 33 - Bordeaux
Metal : bronze
Diameter : 42,9 mm
Orientation dies : 12 h.
Engraver LORTHIOR Pierre-Joseph (1733-1813)
Weight : 38,8 g.
Edge : lisse
Coments on the condition:
Superbe médaille avec de beaux reliefs et un agréable aspect avec cette patine brun sombre et brillante
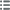
Obverse
Obverse legend : LUD XVI REX CHRISTIANISS.
Obverse description : Buste de profil tourné vers la gauche.
Reverse
Reverse legend : RAFFINERIES REVIVIFIÉES ARRÊT DU 25 MAI 1786 // PRÉSENTÉ / AU ROI / PAR LES / RAFFINEURS/ DE / BORDEAUX.
Reverse description : Légende circulaire et en 6 lignes dans une couronne de roseaux.
Commentary
Médaille signée LORTHIOR F. pouvant être d’époque ou issu d’une frappe plus tardive (avant 1832). Nous restons incertains à ce sujet.
Pierre-Joseph Lorthior, ou Lorthioir, né le 22 janvier 1733 à Lille et mort en 1813 à Paris, est un médailleur et dessinateur de billet de banque français. Il a gravé un grand nombre de médailles, cachets et jetons. C’test lui qui exécuta le grand sceau de la reine Marie-Antoinette d'après les étains de M. Richebé. Il était médailleur du roi.
En 1789, il exécute différentes gravures pour des billets de la Caisse d'escompte. En 1790, il envoie à l'Assemblée nationale un rapport sur la confection des assignats et son projet est retenu pour une première série d'émissions. En 1791, il participe au concours national visant à refondre l'ensemble des pièces de monnaie. Il est l'auteur de plusieurs assignats, aux côtés de Nicolas-Marie Gatteaux.
Depuis le XVIIe siècle, les Bordelais se sont familiarisés avec les routes atlantiques vers les îles tropicales. Les armateurs et la Royale y transportèrent d’innombrables marins, aventuriers, militaires, négociants qui rapportèrent des souvenirs de délices parfumés, trop fragiles pour être transportés : ananas, mangues, bananes. Mais la canne à sucre, culture exigeante en main-d’œuvre peut être malaxée sur place ; le sucre extrait se transforme en épaisse et collante mélasse. Les pains de sucre au goût de miel migrèrent alors vers les rivages aquitains, sous forme de blocs cristallisés dans les moules coniques provenant de poteries telle celle très active de Sadirac en Entre-deux-Mers. Un exquis dérivé, le rhum connut un durable succès… Cette industrie de raffinage s’installa très tôt dans la cité puisque la première autorisation d’établir une raffinerie fut accordée par les jurats en 1633. En 1740 la production de sucre atteint
1 000 tonnes !
Un siècle plus tard, 35 raffineries fonctionnaient, dont Abribat, Bordes, Cardes, Bazille, Michelot… bientôt supplantées par l’usine Saint-Rémi qui s’équipa de modernes machines à vapeur. En 1850, elle fournira 15 % de la consommation des sucres et mélasses de l’Europe. Mais après 1880, s’impose la concurrence de la culture betteravière. Le nombre des raffineries de sucre fut réduit alors à trois : ne restaient que Saint-Rémi, Frugès et Tivoli / Sainte-Croix.
Pierre-Joseph Lorthior, ou Lorthioir, né le 22 janvier 1733 à Lille et mort en 1813 à Paris, est un médailleur et dessinateur de billet de banque français. Il a gravé un grand nombre de médailles, cachets et jetons. C’test lui qui exécuta le grand sceau de la reine Marie-Antoinette d'après les étains de M. Richebé. Il était médailleur du roi.
En 1789, il exécute différentes gravures pour des billets de la Caisse d'escompte. En 1790, il envoie à l'Assemblée nationale un rapport sur la confection des assignats et son projet est retenu pour une première série d'émissions. En 1791, il participe au concours national visant à refondre l'ensemble des pièces de monnaie. Il est l'auteur de plusieurs assignats, aux côtés de Nicolas-Marie Gatteaux.
Depuis le XVIIe siècle, les Bordelais se sont familiarisés avec les routes atlantiques vers les îles tropicales. Les armateurs et la Royale y transportèrent d’innombrables marins, aventuriers, militaires, négociants qui rapportèrent des souvenirs de délices parfumés, trop fragiles pour être transportés : ananas, mangues, bananes. Mais la canne à sucre, culture exigeante en main-d’œuvre peut être malaxée sur place ; le sucre extrait se transforme en épaisse et collante mélasse. Les pains de sucre au goût de miel migrèrent alors vers les rivages aquitains, sous forme de blocs cristallisés dans les moules coniques provenant de poteries telle celle très active de Sadirac en Entre-deux-Mers. Un exquis dérivé, le rhum connut un durable succès… Cette industrie de raffinage s’installa très tôt dans la cité puisque la première autorisation d’établir une raffinerie fut accordée par les jurats en 1633. En 1740 la production de sucre atteint
1 000 tonnes !
Un siècle plus tard, 35 raffineries fonctionnaient, dont Abribat, Bordes, Cardes, Bazille, Michelot… bientôt supplantées par l’usine Saint-Rémi qui s’équipa de modernes machines à vapeur. En 1850, elle fournira 15 % de la consommation des sucres et mélasses de l’Europe. Mais après 1880, s’impose la concurrence de la culture betteravière. Le nombre des raffineries de sucre fut réduit alors à trois : ne restaient que Saint-Rémi, Frugès et Tivoli / Sainte-Croix.








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data



