E-auction 291-211518 - fme_412048 - III REPUBLIC Médaille de mérite des Arts Décoratifs
You must signin and be an approved bidder to bid, LOGIN TO BID. Accounts are subject to approval and the approval process takes place within 48 hours. Do not wait until the day a sale closes to register. Clicking on « bid » constitutes acceptance of the terms of use of cgb.fr private e-auctions.
Bids must be placed in whole Euro amounts only. The sale will start closing at the time stated on the item description; any bids received at the site after the closing time will not be executed. Transmission times may vary and bids could be rejected if you wait until the last second. For further information ckeck the E-auctions F.A.Q.
NO BUYER'S FEE.
NO BUYER'S FEE.
| Estimate : | 120 € |
| Price : | 21 € |
| Maximum bid : | 30 € |
| End of the sale : | 12 November 2018 18:52:00 |
| bidders : | 7 bidders |
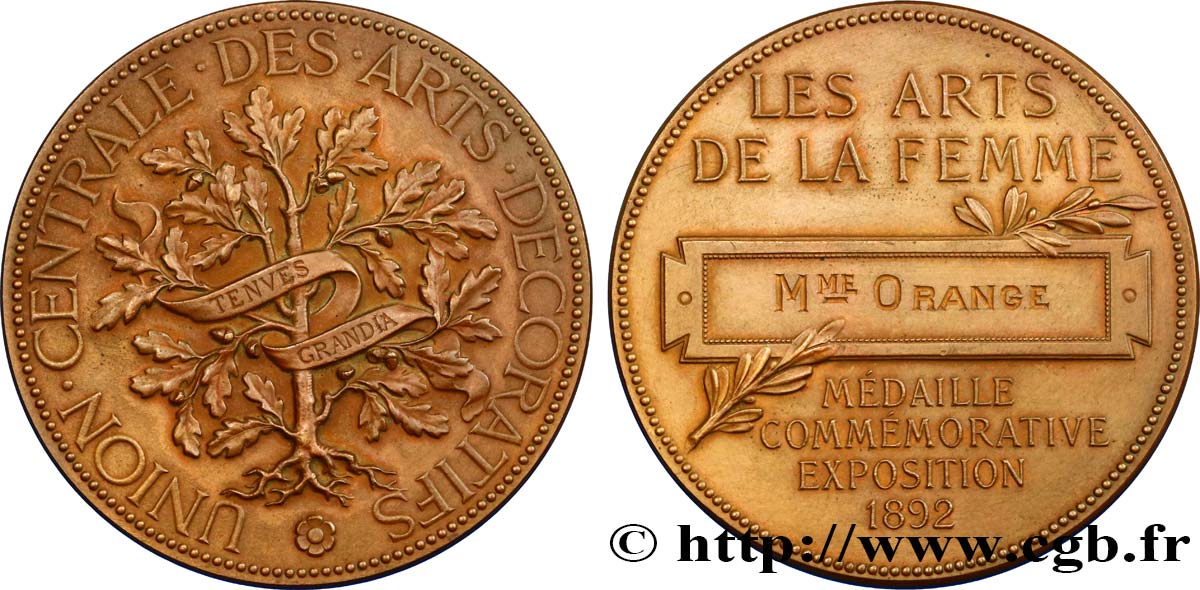
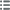
Type : Médaille de mérite des Arts Décoratifs
Date: 1892
Mint name / Town : 75 - Paris
Metal : bronze
Diameter : 50,5 mm
Orientation dies : 12 h.
Weight : 50 g.
Edge : lisse
Coments on the condition:
Très belle médaille avec une agréble patine, dans sa boîte ronde en carton
Obverse
Obverse legend : UNION CENTRALE DES ART DÉCORATIFS.
Obverse description : Chêne avec un ruban inscrit TENVES GRANDIA ; légende autour.
Reverse
Reverse legend : LES ARTS /DE LA FEMME // MÉDAILLE / COMMÉMORATIVE / EXPOSITION / 1892.
Reverse description : Légende en 6 lignes autour d’un cartouche avec deux petites branches de lauriers.
Commentary
Médaille décernée à Mme Orange, mais non signée.
Le Comité des dames est né en 1895 par la volonté de l’Union centrale des arts décoratifs (UCAD) d’encourager et d’encadrer le travail féminin dans les arts décoratifs. Sa création se situe en effet dans un contexte de débats sur la place des femmes dans la société : le travail féminin, de plus en plus visible, est observé avec méfiance, accusé de perturber l’ordre social par une concurrence déloyale au travail masculin, et de troubler l’ordre familial en enlevant la femme à ses tâches ancestrales d’épouse et de mère...
Néanmoins, les études supérieures et les professions qualifiées s’ouvrent progressivement aux femmes. La sphère artistique ne reste pas à l’écart de ces débats et de ces progrès. Tandis que l’École des beaux-arts et l’École des arts décoratifs deviennent accessible aux femmes dans les années 1890, les travaux d’art féminins sont considérés comme une source honorable de revenus et font l’objet d’un intérêt plutôt bienveillant, quoique souvent condescendant. Ainsi, une première grande exposition en 1892 au Palais de l’industrie, sous le commissariat de l’UCAD, est consacrée aux arts de la femme. En 1893, l’Exposition universelle de Chicago accueille le « Woman’s Building », une exposition féminine dont la section française est organisée par Mme Pégard, future initiatrice du Comité des dames de l’UCAD.
cf. http://www.lesartsdecoratifs.fr/francais/bibliotheque/expositions/archives/presentation-3095.
Le Comité des dames est né en 1895 par la volonté de l’Union centrale des arts décoratifs (UCAD) d’encourager et d’encadrer le travail féminin dans les arts décoratifs. Sa création se situe en effet dans un contexte de débats sur la place des femmes dans la société : le travail féminin, de plus en plus visible, est observé avec méfiance, accusé de perturber l’ordre social par une concurrence déloyale au travail masculin, et de troubler l’ordre familial en enlevant la femme à ses tâches ancestrales d’épouse et de mère...
Néanmoins, les études supérieures et les professions qualifiées s’ouvrent progressivement aux femmes. La sphère artistique ne reste pas à l’écart de ces débats et de ces progrès. Tandis que l’École des beaux-arts et l’École des arts décoratifs deviennent accessible aux femmes dans les années 1890, les travaux d’art féminins sont considérés comme une source honorable de revenus et font l’objet d’un intérêt plutôt bienveillant, quoique souvent condescendant. Ainsi, une première grande exposition en 1892 au Palais de l’industrie, sous le commissariat de l’UCAD, est consacrée aux arts de la femme. En 1893, l’Exposition universelle de Chicago accueille le « Woman’s Building », une exposition féminine dont la section française est organisée par Mme Pégard, future initiatrice du Comité des dames de l’UCAD.
cf. http://www.lesartsdecoratifs.fr/francais/bibliotheque/expositions/archives/presentation-3095.








 Report a mistake
Report a mistake Print the page
Print the page Share my selection
Share my selection Ask a question
Ask a question Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Full data
Full data



